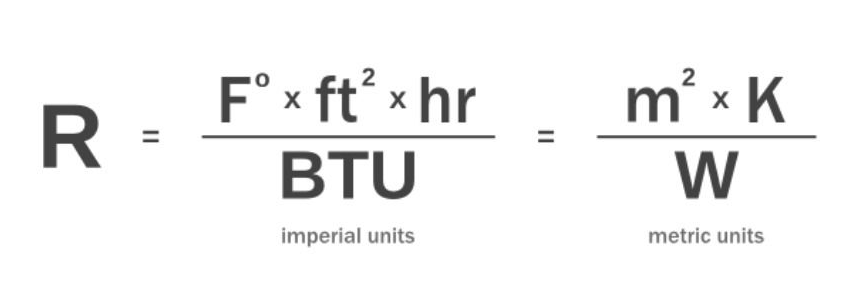While choosing the thermal insulation materials, you can’t ignore this key factor, R-value. To many users, the R-value tells directly how is the thermal efficiency of the insulation. To choose the right insulation material, it’s essential to clarify the following questions: what is the R-value for insulation? and what is the best R-value for your insulation project?
1. What is the R-value of insulation?
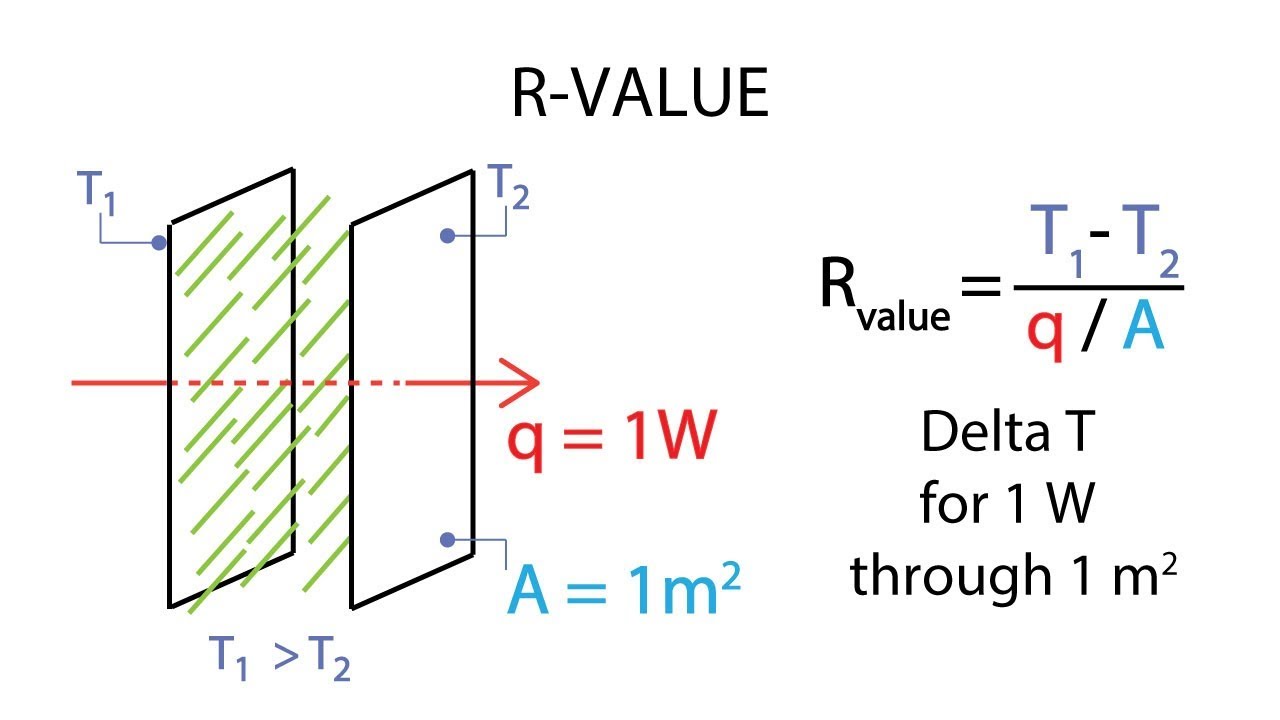
The R-value measures how much resistance the insulation has to heat flow. The higher the R-value, the more heat the insulation material can preserve and the better is the insulation effect. Naturally, insulation materials with higher R-values cost more than ones with lower R-values.
To calculate the R-value, you need to divide the thickness of the material (in meters) by the thermal conductivity (in W/mK). The formula is the following:
Where: L refers to the thickness of their material in meters; λ refers to the thermal conductivity in W/mK. As shown in the formula, R-value is directly proportional to the material thickness and inversely proportional to the thermal conductivity.
Thermal Conductivity to R-value
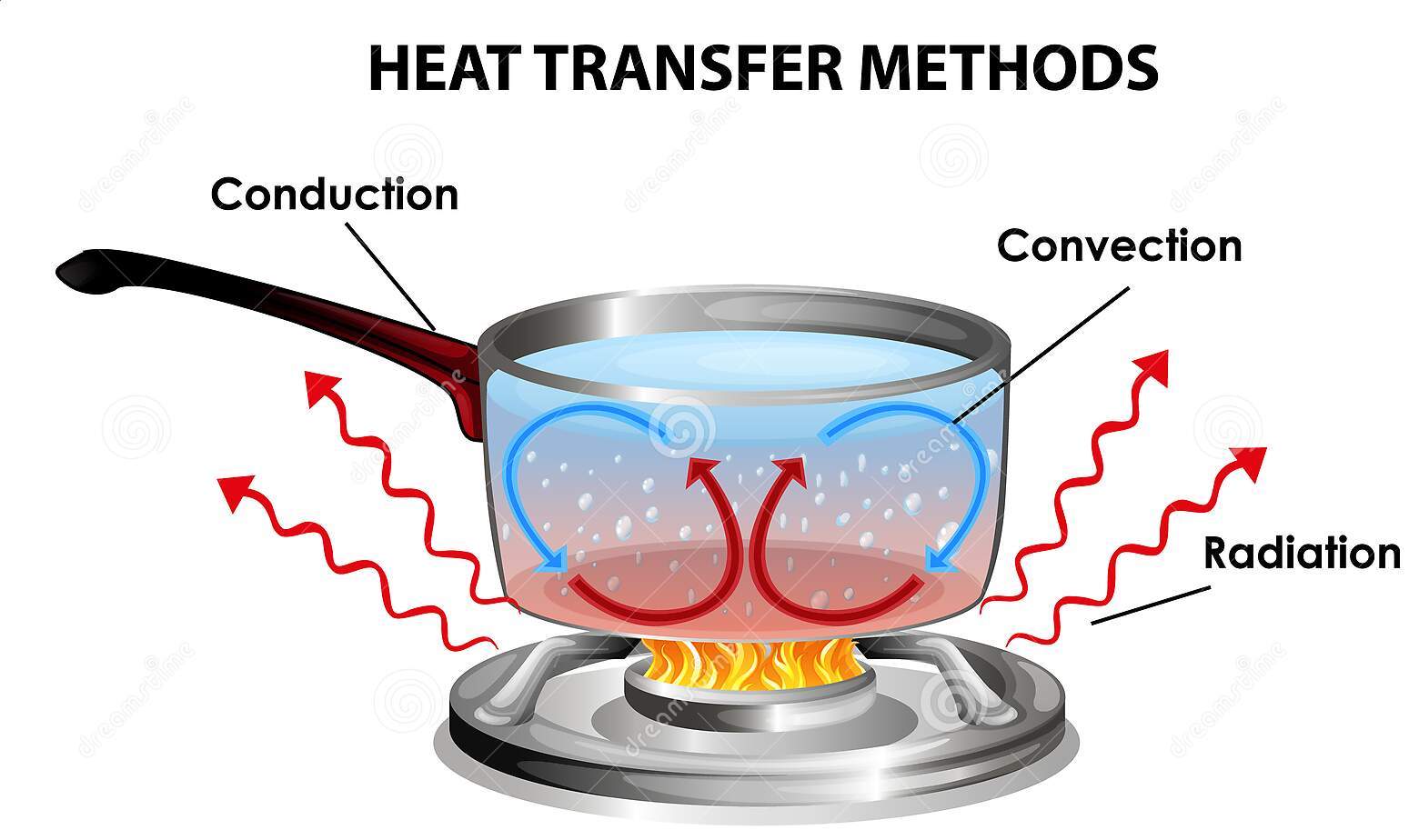
In summary, mainly there are three methods of heat transfer: radiation, convection and
conduction. This thermal conductivity occurs through molecular agitation and contact: more specifically, heat moves from an area of high molecular mobility and high temperature to an area with lower molecular mobility and naturally, low temperature. This whole conduction process will be completed until the thermal equilibrium is reached. And during the whole process, the rate at which heat is transferred will be expressed in thermal conductivity. This thermal conductivity is also defined as the amount of heat per unit time per unit area that can be conducted through a sheet of unit thickness of a given material.
Thermal conductivity is dependent on three factors: the temperature gradient leading to the heat transfer; the properties of the material and the path length that the heat follows, which determine the rate of the heat transfer (thermal conductivity). That is to say, thermal conductivity is an intrinsic ability of a material to transfer or conduct heat.
Thermal conductivity is quantified in W/mK (watts per meter degree Kelvin), according to the International Systems of Unit (SI unit). As we mentioned above, it’s the reciprocal of R-value (thermal resistance), which measures the resistance of the material to the heat flow.
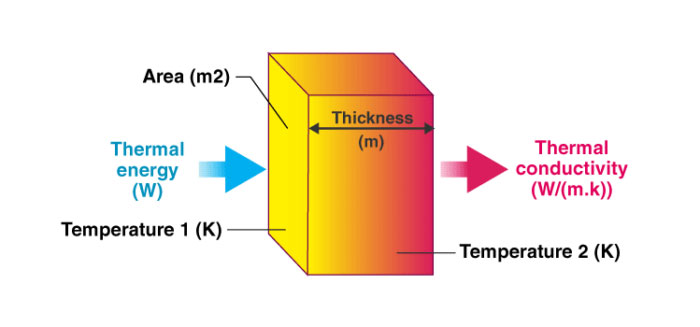
The equation of thermal conductivity is the following:
k=Q∗L/A(T2−T1)
Where: Q = heat flow (W)
L = length or thickness of the material (m)
A = surface area of material (m2)
T2−T1 = temperature gradient (K)
The thickness of material vs R-value
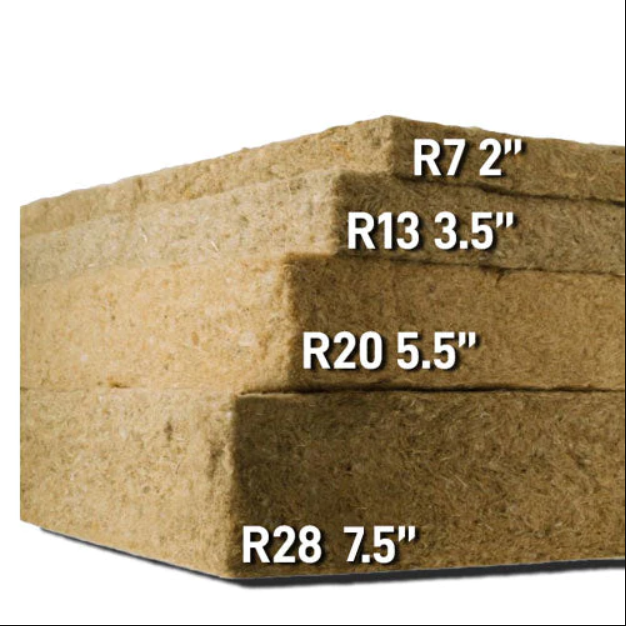
R-value is directly proportional to the thickness of the material. Supposedly, the thicker the insulation, the higher the R-value and the better the insulation material’s performance.
However, this isn’t necessarily true. Sometimes the insulation materials need to be compressed for specific packaging requirements: for example, the thermal insulation manufacturer has to compress the fiberglass insulation below the labeled thickness for safe packaging and transportation to the client; however, when the insulation material is applied by the user, its thickness is reduced due to the compression and consequently, this R-value of fiberglass insulation is reduced, too.
To resolve this problem, make sure that the wall cavities have a depth greater than the labeled thickness of the insulation material. In this way, there will be no compression and therefore no reduction of the R-value.
Metric R-value vs Imperial R-Value
It’s worth mentioning that there are two different systems of thermal resistance: the RSI and the R-value. The RSI value is a metric system unit (m2 K/W) while the R-Value is an imperial system unit (ft2°F·h/BTU).
Both the R-value of fiberglass insulation and the rock wool R-value are designed to fit into the framed cavity without reducing the labeled thickness. On the other hand, the R-value of foam rubber or other rigid board type is rated by RSI value per millimeter or R-value per inch.
Here’s the tip for converting between these two units of measurement:
To convert an RSI Value to an R-Value, multiply the RSI Value by 5.678.
To convert an R-Value to an RSI Value, divide the R-Value by 5.678.
2. What is the best R-value for insulation?
What is the best R-value for insulation? To answer this question, you need to take many factors into account. Mainly the main determining factors are the following:
(1). Types of insulation materials
In this part, while talking about types of insulation materials, we mainly refer to different forms of insulation materials. As we mentioned before, heat resistance is an intrinsic ability of the material, depending on the properties of the material, which include the form and interior texture of the material.
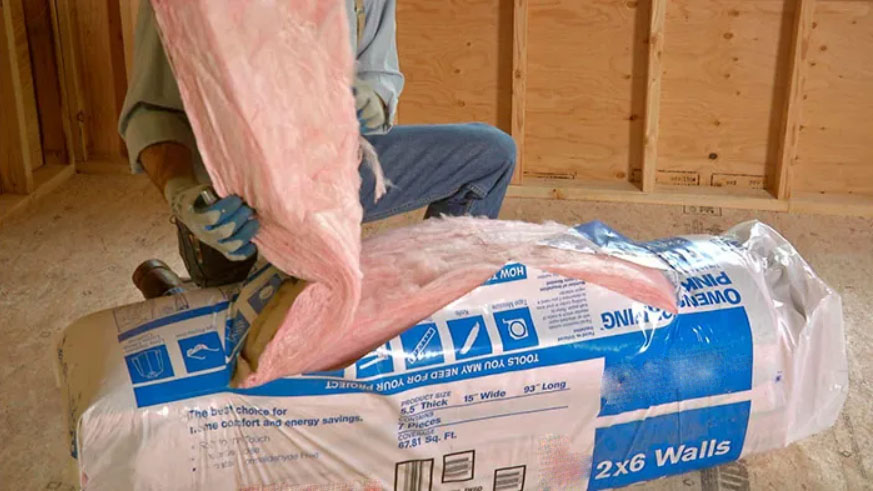
Blanket batts and rolls–These are the most commonly used forms of insulation materials. They are mainly made of fiberglass or other mineral wool. Compared with other forms of insulation material, their thickness is relatively higher rendering a higher heat resistance. Besides, they’re pretty easy to install.
Rigid board– Compared with blanket batts and wools, the rigid board comes with a lesser thickness, which might make it less resistant to heat. However, the cells inside the material help trap air and resist conductive heat flow. Moreover, its texture of high density provides more protection and it can serve as an air and moisture barrier. For example, the foam rubber padding is widely used to insulate the exterior walls, the underfloor or the roof assemblies, etc.
Loose-fill or blown-in – Compared with the blanket batt or the rigid board, the loose-fill insulation material is incredibly pliable, which makes it more suitable for hard-to-reach areas, such as ceiling insulation or crawl space insulation, etc.
(2). Your demand for insulation
Generally, there are three main applications of thermal insulation: residential application, commercial application and industrial application. Apart from the industrial application that has special requirements, both the residential and the commercial applications depend on basically the structure of the construction. More specifically, the dimensions of the cavity (wall, floor, ceiling, crawl spaces) determine how much R-value can be installed: the thickness of the cavity created by framing in the home will determine and limit the choices of R-value that can be installed; however, in terms of the cavity whose thickness isn’t constrained, such as attic, floors and crawl spaces, the larger R-value of insulation can be used to provide higher levels of energy savings and comfort.
Besides, you also need to take other factors into account while determining the R-value of insulation, such as indoor air quality impacts, life cycle costs, ease of installation, etc.
3. R-value of different types of insulation material
As a professional thermal insulation supplier, ECOIN provides insulation products of different materials and in different forms. There are four primary types of insulation with a wide range of R-values for insulation to meet your demand.
R-value of fiberglass insulation
Fiberglass insulation, also known as glass mineral wool, is the most commonly used insulation material. Depending on the type of glass mineral wool you use-batt, loose-fill, or rigid board, this R-value of fiberglass insulation ranges from 2.2-4.3 per inch.
Forms of material | R-value (per inch of thickness) |
Blanket batts | 1.5-4.2 |
Loose-fill | 2.2-4.3 |
| Rigid board | 4-5 |
As we mentioned before, sometimes the thermal insulation manufacturer needs to compress the glass mineral wool for the packaging and transportation, which might reduce the R-value for fiberglass insulation for the user to apply. In terms of this issue, ECOIN promises that the R-value of fiberglass insulation you get is the same as the labeled value.
For more information, please click: Ecoin Fiberglass Insulation
R-value of Rock Wool
Compared with fiberglass insulation, rock wool offers a higher R-value: the average rock wool R-value maintains above 3.0 to 3.3 per inch of thickness. The rock wool batt provides far greater thermal efficiency, heat retention, moisture resistance, and sound-dampening capabilities. Moreover, this rock wool R-value usually remains stable throughout the entire lifespan of the building. Naturally, this rock wool batt costs slightly more than other common insulation materials such as fiberglass insulation blankets.
For more information, please click: Ecoin Rock Wool
R-value of ceramic wool
Unlike the glass mineral wool or the rock wool batt, the ceramic wool blanket is not typically used for residence or other construction projects. This ceramic wool blanket is widely used in the industry, such as furnaces and kiln linings, etc. For this reason, some ceramic wool blankets might have an R-value of 5 per inch thickness.
However, in most occasions, this ceramic wool R-value isn’t explicit on the package. Among every eight ceramic wool blanket products, only two are listed with an average ceramic wool R-value above 2.35 per inch thickness.
For more information, please click: Ecoin Ceramic Wool
R-value of Foam Rubber
There’s a wide range of R-values of foam rubber, from 3.6 per inch to 8.0 per inch. This R-value for foam rubber varies depending on the prime material and the texture of the foam rubber padding: generally speaking, the R-value of foam rubber with closed cells is higher than the R-value of foam rubber with open cells.
Besides the closed-cell foam rubber padding is more water resistant than the foam rubber padding with open cells.
For more information, please click: Ecoin Rubber Foam