1. What is foam rubber?
Foam rubber, also known as cellular, sponge, or expanded rubber, refers to the kind of rubber manufactured with a foaming agent to create an air-filled matrix structure. This blowing agent usually is a gas or a chemical that produces a gas. Thus, a mass of bubbles is created in the material.
There are different types of foaming agents, which determine the flexibility and rigidity of the foam rubber. Typically, foam rubber with high flexibility uses carbon dioxide gas while some foam rubber with high rigidity uses HFCs and HCFCs. In terms of ECOIN’s foam rubber insulation products, we offer foam rubber sheets or foam rubber tubes without the use of CFCs nor HCFCs, which makes our product environmentally- friendly.
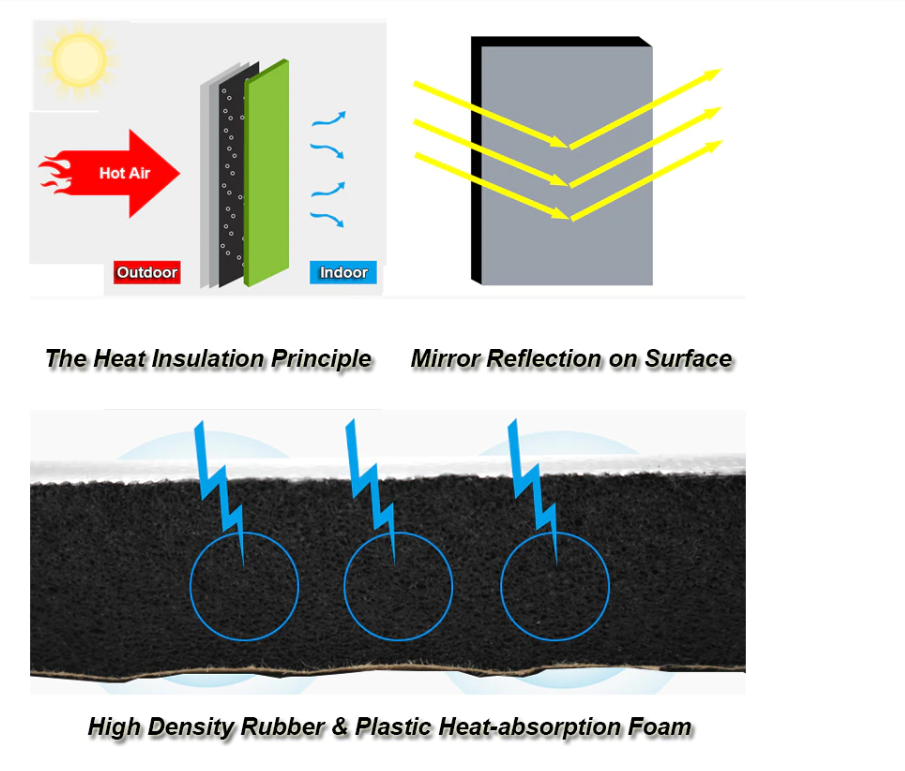
In terms of its thermal conductivity, foam rubber is a poor conductor of heat and an excellent insulator: the electrons in the rubber are tightly bound; hence, they aren’t free for heat conduction. The R-value of the rubber is high. Besides, the structure of the foam rubber helps to block heat conduction:
The cells inside the foam rubber hold off the transfer of heat very well;
The foam rubber is characterized by high heat resistance;
The foam rubber is resistant to a compression set, even after strenuous heat exposure.
2. What is foam rubber made of?
Materials of the foam rubber
In terms of the material, there are many types of foam rubber: neoprene foam, EPDM foam, polyurethane foam, PVC rubber, and NBR rubber, etc. Basically, the neoprene foam sheet, the PVC rubber sheet, and the NBR rubber sheet are the most useful products for thermal insulation.
The NBR is characterized by good oil- and fuel resistance. On the other hand, PVC has good resistance to UV rays, chemicals, and fire. More importantly, PVC material is a more cost-effective choice.
Cell Structures of foam rubber
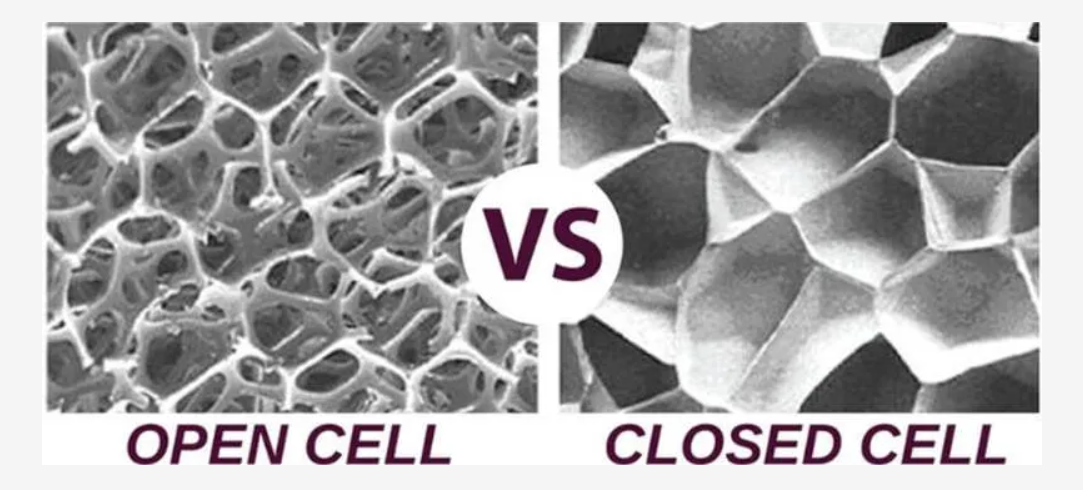
In terms of cell structure, there are two main types of foam rubber: closed-cell foam and open-cell foam.
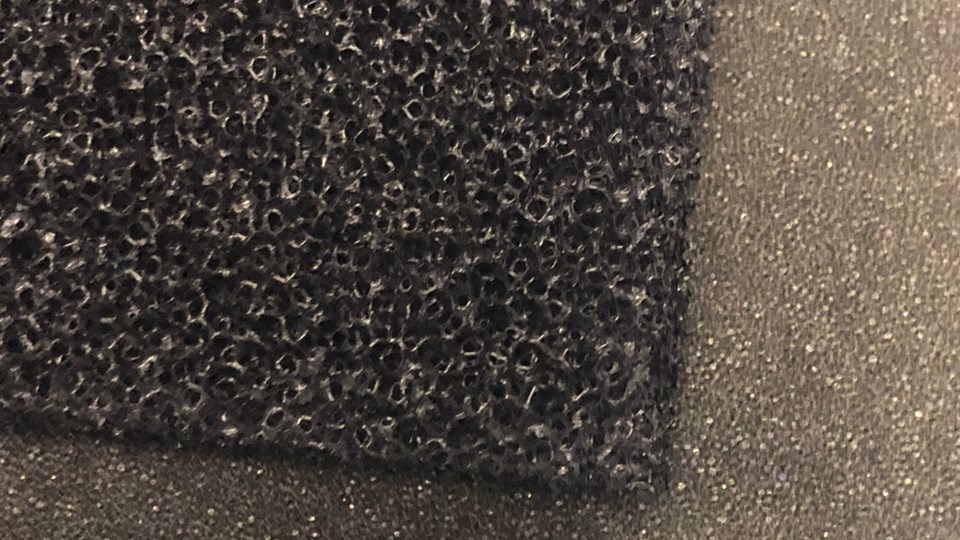
The open-cell foam rubber is composed of cells that are not totally enclosed by its walls and are open to the surface either directly, or by interconnecting with other cells. Due to this cell structure, the open-cell foam rubber is more flexible than the closed-cell rubber foam sheet; however, on the other hand, this open-cell rubber foam material has a higher ability of absorption allowing whatever liquid or gaseous media to pass through, which makes it poor for sealing or insulating applications.
In contrast to the open cell foam, the closed cell foam rubber material is composed of cells that are entirely enclosed by its walls and not interconnecting with other cells. This structure helps to reduce liquid and gas flow, which makes the closed-cell rubber foam sheet appropriate for sealing and insulation. It’s worth mentioning that, unlike the open cell foam rubber, the closed-cell rubber foam sheet can be manufactured in a range of densities.
To sum up, the features of open-cell foam and closed-cell foam are the following:
| Open & Closed Cell Foam | Features |
| Closed Cell Foams: EPDM NeopreneNBR (Nitrile) Neoprene/SBR/EPDM Blend PVC/NBR Blend PVC Foam | With excellent resistance to ozone, UV, weather and high temperatures. With stability under exposure to oils, ozone, and weathering resistance. For this reason, it can be widely used for many industrial applications With good resistance to moisture and other kinds of fluids. |
| Open Cell Foams: Neoprene Natural Rubber | With higher ability of absorption of sound, vibration, and dampening |
3. What are the advantages of foam rubber insulation?
As we mentioned before, foam rubber insulation is the main material of closed-cell rubber foam, which makes it an ideal choice for thermal insulation. The reasons are the following:
Low thermal conductivity– As we mentioned before, the rubber itself is a poor heat conductor and an excellent insulator. Compared with other materials, the R-value of foam rubber is relatively higher.
Stability in harsh environments–Thanks to its closed cell structure, the foam rubber for insulation material is of better structure strength, which allows them to sustain stability (with less swelling) in oil, water, and other liquids. This makes the closed-cell rubber foam sheet or the rubber pipe lagging appropriate for industrial insulations.
Impervious to bacteria, mildew, and rot– Thanks to its closed-cell foam structure, both the closed-cell rubber foam sheet and the rubber pipe lagging don’t absorb water and can resist moisture. This waterproof advantage is even more important for the rubber foam tube as it’s mainly used for pipelines transporting liquid.
Longer lifespan – All the features we mentioned above give the foam rubber a better resistance to various factors that might corrode the foam rubber insulation. And this makes the foam rubber works for a longer period in the thermal insulation.
Nowadays foam rubber insulation isn’t only used in construction to help insulate people’s homes; it’s also used in many industrial applications, such as HVAC system insulation, etc.
4. What kinds of foam rubber products does ECOIN provide?
As a professional rubber foam supplier, ECOIN has always been dedicated to offering you products of high quality and one-stop service, including slitting service, etc.
Generally speaking, ECOIN offers two types of foam rubber insulation:
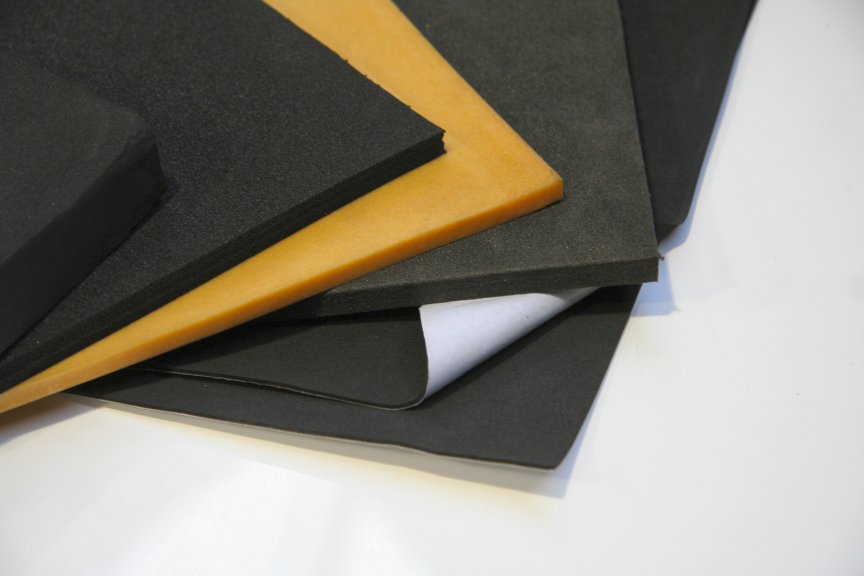
Foam Rubber Sheet– As an experienced rubber foam sheet supplier, we offer foam rubber sheets of different materials, such as EPDM foam sheets, neoprene foam sheets, NBR rubber sheets, and PVC rubber sheets, etc. Our main products are NBR rubber sheets and PVC rubber sheets, which are all synthetic rubber materials.
It’s worth mentioning that our foam rubber sheet is free of CFCs or HCFCs, making it environmentally friendly and ensuring the occupants’ health.
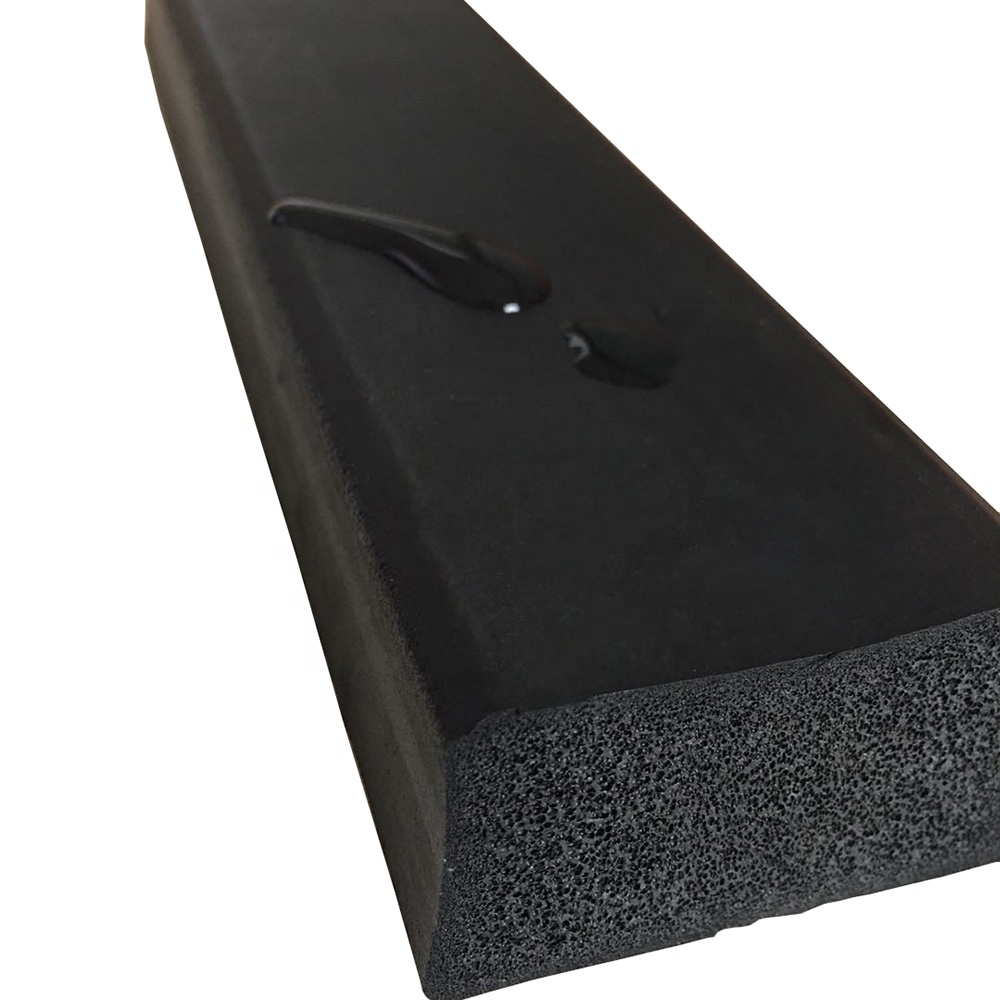
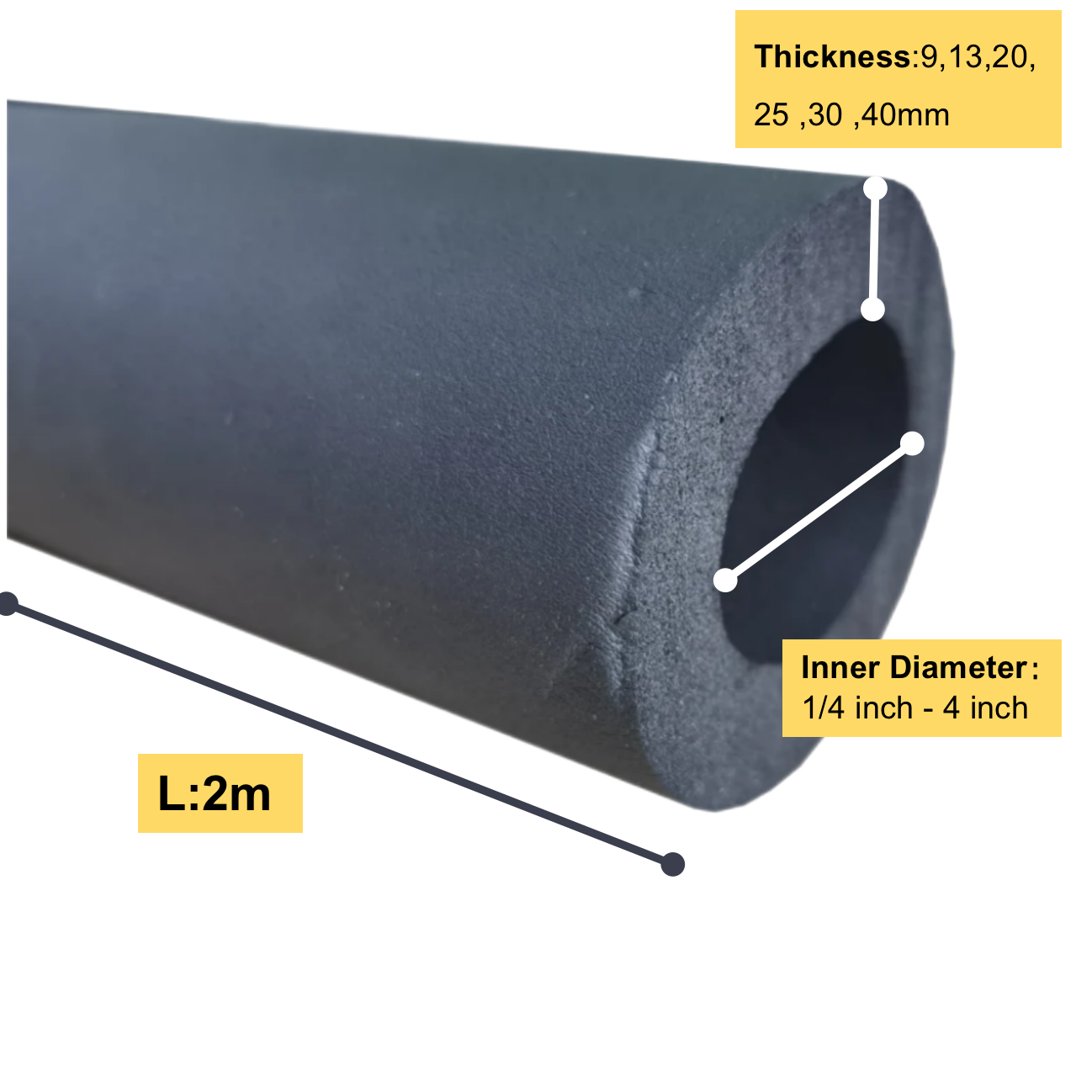
Rubber Foam Pipe Insulation–The foam rubber tube, also known as rubber pipe lagging is another main product of ours. This rubber pipe lagging is widely used in the conditioning or refrigeration system to save energy and prevent condensation.