- Home
- / FAQs
The most important aspect of Ecoin insulation material is its performance – that it consistently provides the designed-for resistance to the passage of heat throughout the lifetime of the building.
Glass Wool FAQ
1.Main material: cullet and sand
2.binder: organic resins
1.No Itchy
2.Good rebount rate (above 90%)
3.Fine fiber (5-6um)
4.Wool evenly weaving
5.if the glass wool can reach above 4 key points, it will has a good thermal conductivity and noise absorption rate.
For metal roof insulation and wall cladding, we recommend 12-24kg/m3 rolls, with the facing of FSK, WMP-VR and HSMAF
1.For duct thermal insulation, we recommend 16-32kg/m3 glass wool rolls and 48kg/m3 boards with the facking of FSK, black FSK.
2.For duct acoustic, we recommend 32kg/m3 rolls and 48kg/m3 boards with the facing of BGT and FGT.
3.For AHU room, we recommend 32kg/m3 rolls with FGT and BGT.
Bulk density, fiber diameter and service temperature.
1.From 10kg-85kg/m3, the heavier the density, the lower thermal conductivity; From above 85kg/m3, thermal conductivity will increase with the increase of density.
2.Thickness won’t effect thermal conductivity. Thickness will effect R value.
3.The finer of the fiber diameter, the better of thermal conductivity.
4.The higher of service temperature, the higher of thermal condutivity.
If the nomal package, the bounce rate is 95%; if the vacuum compressed package, the bounce rate is 80%.
There are 2 units of R-value, the relationship is: 1h•ft2•℉/Btu=5.678m2•℃/w
Glass wool NRC is from 0.85-1.3
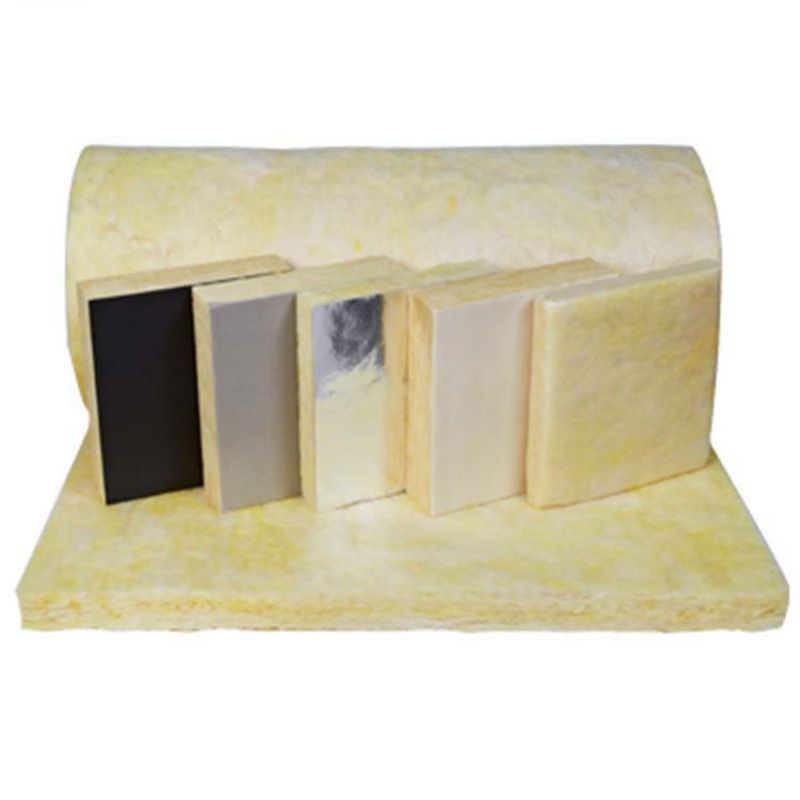
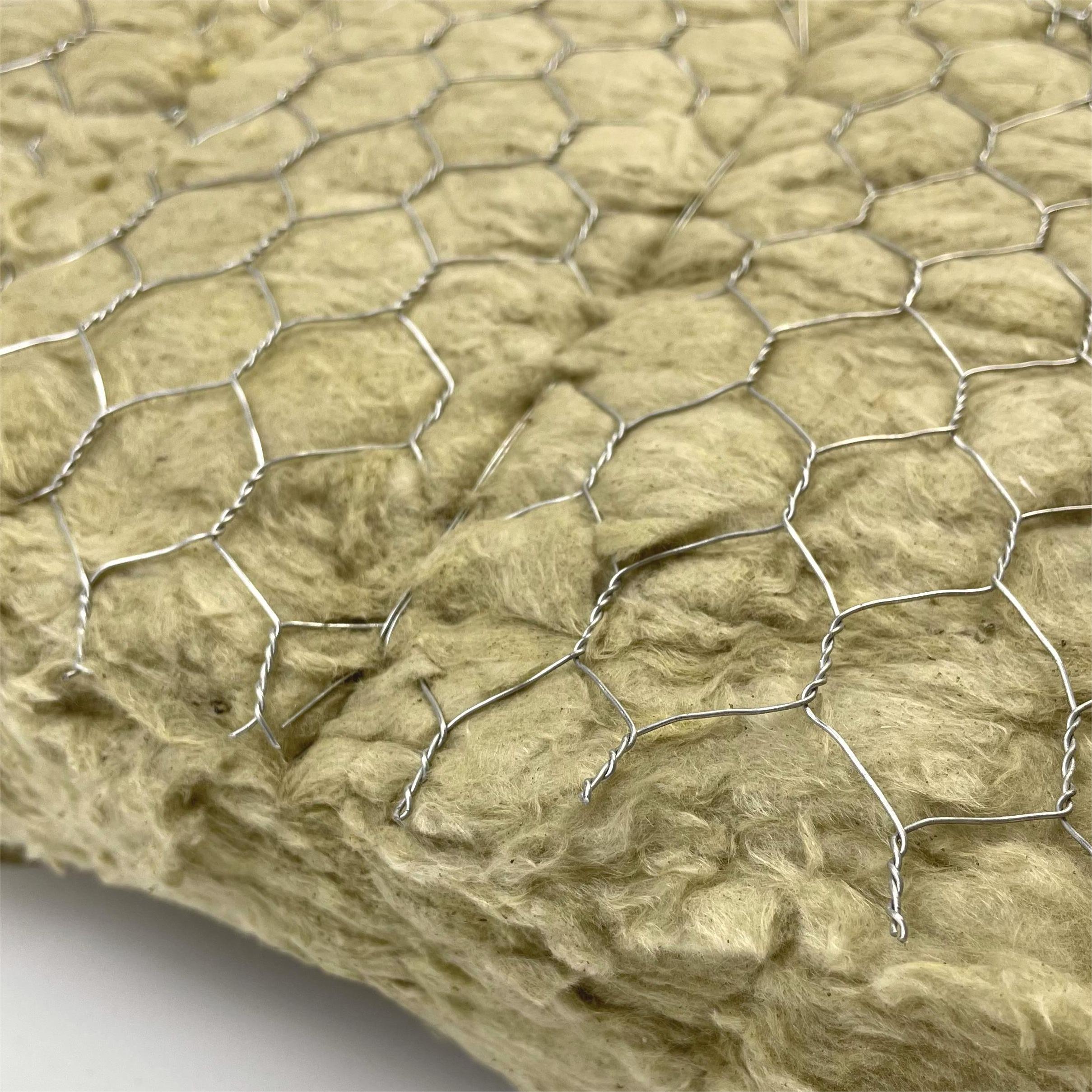
Glass wool is a type of insulation material made from glass fibers arranged into a wool-like texture. It is commonly used for insulation and soundproofing in residential and commercial buildings.
Glass wool insulation is installed in walls, floors, ceilings, and roofs to reduce the transfer of heat between the inside and outside of a building. This helps to keep the building warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer, which can lead to energy savings and lower utility bills.
Glass wool is also used for soundproofing, particularly in recording studios, home theaters, and other spaces where noise control is important. The fibers in glass wool trap sound waves, reducing the amount of noise that travels through walls and ceilings.
In addition to its insulation and soundproofing properties, glass wool is also used for filtration in HVAC systems, as well as for the production of fire-resistant materials. It is a versatile material that is valued for its thermal and acoustic insulation properties, as well as its durability and fire-resistance.
Glass wool is a type of insulating material made from fibers of glass. It is a lightweight, durable, and highly effective insulation material that is used in a wide range of applications, including insulation for buildings, pipes, and industrial equipment.
Glass wool is made by melting glass at a high temperature and then spinning it into fibers using a centrifugal process. These fibers are then collected and formed into a mat or blanket, which can be cut to size and used as insulation.
The structure of glass wool allows it to trap air, which makes it an excellent insulator. It also has a high melting point and is non-combustible, which makes it a safe option for insulation.
Glass wool is available in a range of densities and thicknesses, and can be faced with a variety of materials, including foil, kraft paper, and vinyl. It is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly choice for insulation, as it can be made from recycled glass and is fully recyclable.
Glass wool and fiberglass are similar materials, but they are not exactly the same. Both are made from fine fibers of glass that are used for thermal insulation and soundproofing, but the manufacturing processes and properties of the two materials can differ.
Glass wool is made from glass fibers that are arranged into a wool-like texture. The fibers are typically produced by melting glass and then blowing or spinning the molten glass into fibers. Glass wool is typically used in industrial or commercial applications, such as insulating pipes, ductwork, and machinery.
Fiberglass, on the other hand, is made from glass fibers that are woven or bonded together to create a sheet or mat of material. The fibers are typically produced by a similar process as glass wool, but the fibers are then combined with a binding agent to create a more rigid material. Fiberglass is commonly used in construction, such as for insulation in walls and ceilings, as well as for creating reinforced plastic products like car bodies or boat hulls.
So while both materials are made from glass fibers and used for similar purposes, the way the fibers are manufactured and the resulting properties of the materials can differ.
Yes, glass wool is a good insulator. Glass wool is made of thin fibers of glass that are woven together to create a fluffy material with a high surface area. This structure allows it to trap pockets of air, which are poor conductors of heat and thus help to reduce heat transfer.
Glass wool is often used as insulation in buildings to reduce heat loss in cold climates and to reduce heat gain in hot climates. It is also used as insulation in appliances and industrial equipment. Glass wool has several advantages as an insulation material: it is lightweight, easy to install, and resistant to moisture, mold, and pests. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to some other types of insulation.
However, it is important to note that while glass wool is a good insulator, it can be irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system if proper safety precautions are not taken during installation. Therefore, it is important to follow safety guidelines and wear protective gear when handling and installing glass wool insulation.
The cost of glass wool can vary depending on factors such as the thickness and density of the material, the intended use, and the supplier. In general, glass wool is considered to be an affordable insulation material, particularly when compared to other options such as foam or mineral wool. However, it's important to keep in mind that the cost of installation can add to the overall cost, as well as any additional materials needed for the job. Ultimately, the price of glass wool will depend on the specific circumstances of the project.
Glass wool is a type of insulation material made from spun glass fibers. The fibers are very fine and can be irritating to the skin, causing itching and sometimes even a rash. This is because the fibers are sharp and can pierce the skin, leading to irritation and inflammation. In addition, the fibers are lightweight and can become airborne, leading to inhalation and irritation of the respiratory system.
To avoid the itchiness caused by glass wool, it is important to handle the material carefully and wear appropriate protective gear such as gloves, long sleeves, and a face mask. It is also important to avoid direct contact with the material and to keep the area well-ventilated. If you do come into contact with glass wool and experience itching or other symptoms, it is recommended to wash the affected area with soap and water and seek medical attention if necessary.
Rockwool and glass wool are both types of insulation materials that are commonly used for thermal and acoustic insulation in buildings.
Rockwool, also known as mineral wool, is made from natural basalt rock and is a denser material compared to glass wool. It is highly resistant to fire and is commonly used for soundproofing and thermal insulation in buildings.
Glass wool, on the other hand, is made from recycled glass and is a lighter material compared to Rockwool. It is also highly resistant to fire and is commonly used for thermal insulation in buildings.
Both materials have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two largely depends on the specific application and requirements of the project. Here are some factors to consider when deciding between Rockwool and glass wool:
Thermal insulation: Both Rockwool and glass wool are excellent thermal insulators, but Rockwool has a slightly higher R-value (measure of thermal resistance) per inch of thickness, which means it provides better insulation per unit of thickness.
Soundproofing: Both materials are effective at soundproofing, but Rockwool is denser and provides better sound absorption compared to glass wool.
Fire resistance: Both materials are highly resistant to fire, but Rockwool is more fire-resistant than glass wool.
Cost: Glass wool is generally less expensive compared to Rockwool.
In summary, both Rockwool and glass wool are good insulation materials with their own advantages and disadvantages. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the project.
Glass wool is a type of insulation material made from spun glass fibers, and it is designed to be fire-resistant. While glass wool can be damaged or destroyed by fire, it does not easily ignite and is not considered a significant fire hazard.
In fact, many building codes and safety regulations require the use of fire-resistant insulation materials like glass wool in certain applications, such as in commercial buildings and multi-family residential buildings. This is because fire-resistant insulation materials can help slow the spread of fire, giving occupants more time to evacuate and reducing property damage.
However, it's worth noting that while glass wool itself is not highly flammable, it can still be a potential fire hazard if it becomes contaminated with other flammable materials, such as oils or greases. Additionally, if glass wool is used improperly or installed incorrectly, it can create gaps or spaces where fire can spread more easily.
Therefore, it's important to follow proper safety guidelines when using glass wool insulation or any other building materials.
Glass wool does not contain asbestos. Asbestos is a naturally occurring mineral that was commonly used in building materials and insulation products in the past. However, due to the health risks associated with asbestos exposure, its use has been largely phased out in modern construction materials and replaced with safer alternatives, such as glass wool.
Glass wool is a type of insulation material made from recycled glass that has been melted and spun into thin fibers. It is commonly used for thermal and acoustic insulation in buildings, and is considered to be a safe and effective alternative to asbestos-containing insulation products. However, it's important to note that like any other insulation material, glass wool can pose a health risk if it is not installed or handled properly. Appropriate safety measures, such as wearing protective clothing and a respirator, should be taken when working with any type of insulation material.
Glass wool, also known as fiberglass insulation, can potentially cause irritation and discomfort if it comes into contact with the skin or is ingested or inhaled.
Direct contact with fiberglass insulation can cause skin irritation, redness, and itching. Inhaling fiberglass fibers can also cause respiratory irritation, coughing, and difficulty breathing. Fiberglass fibers are very small and can be easily inhaled, which is why it's important to wear appropriate protective gear such as gloves, long sleeves, pants, and a respirator when working with fiberglass insulation.
In addition to the physical irritation, some people may also have an allergic reaction to fiberglass insulation. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can include itching, redness, and swelling at the point of contact, as well as hives, difficulty breathing, and wheezing.
Therefore, it is important to take proper precautions and wear protective gear when handling glass wool, and to seek medical attention if you experience any adverse symptoms.
Inhalation of glass wool fibers can cause irritation to the respiratory system, leading to symptoms such as coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Long-term exposure to glass wool fibers may increase the risk of lung diseases such as bronchitis and fibrosis. Skin contact with glass wool may cause itching and irritation. It is important to use appropriate personal protective equipment when handling glass wool to minimize these risks.
It is generally not recommended to touch glass wool with bare hands as it can cause irritation and small particles can break off and get lodged in the skin, causing discomfort. Glass wool is made from fine fibers of glass and can be irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system if inhaled.
If you need to handle glass wool, it is recommended to wear protective gloves, a long-sleeved shirt, and a dust mask to prevent the fibers from coming into contact with your skin or being inhaled. Additionally, it is important to dispose of glass wool properly and avoid scattering it, as the fibers can pose a health hazard if they become airborne.
No, glass wool does not rot. It is an inorganic material made of glass fibers that do not decay or decompose over time.
Glass wool can last for several decades without significant degradation or loss of insulation performance, as long as it is installed properly and not subjected to damage or moisture.
Glass wool is a type of insulation material made from glass fibers that are formed into a wool-like texture. While it is not specifically designed for soundproofing, it can help reduce the transmission of sound to some extent.
When sound waves encounter a barrier, some of the energy is absorbed, and some of it is reflected. Glass wool, being a porous material, can absorb some of the sound waves that come into contact with it. However, its effectiveness in blocking sound depends on several factors, such as the thickness of the material, the frequency of the sound waves, and the construction of the surrounding walls or partitions.
Overall, while glass wool can provide some level of sound absorption and reduction, it may not be the most effective option for soundproofing. Other materials, such as acoustic foam or mass loaded vinyl, may be more suitable for that purpose.
Glass mineral wool insulation can be itchy and irritating to the skin. This is because the fibers in glass mineral wool insulation are very small and can easily become airborne, leading to skin irritation and respiratory problems if inhaled. It is important to wear proper protective gear, such as gloves and a dust mask, when handling glass mineral wool insulation to prevent irritation and other health hazards. Additionally, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer's safety data sheet (SDS) and follow their recommended safety precautions when handling any type of insulation material.
The R-value of glass wool insulation depends on its thickness, density, and other factors. Generally, the R-value of glass wool insulation ranges from R-2.5 to R-3.7 per inch (R-10 to R-15 for a standard 4-inch thickness). However, some higher-density glass wool insulation can have an R-value of up to R-4.3 per inch (R-17 for a standard 4-inch thickness). It is important to note that the R-value of insulation is a measure of its thermal resistance, and the higher the R-value, the more effective the insulation is at reducing heat flow.
In general, glass mineral wool insulation is not considered toxic, as it is made primarily of natural materials like sand and recycled glass. However, like any type of insulation, it is important to follow proper safety precautions when handling glass mineral wool to avoid irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. It is recommended to wear protective clothing, gloves, safety glasses, and a mask when installing or handling glass mineral wool insulation.
The best way to remove glass wool from skin is to use adhesive tape or a lint roller to gently lift the fibers off the skin. Do not use water or try to pull the fibers out with your fingers, as this can cause the fibers to embed deeper in the skin or break, making them harder to remove. If you experience any itching, redness, or discomfort, seek medical attention.
Yes, it is recommended to wear gloves when handling glass wool to protect your skin from irritation and potential injury. Glass wool is made from thin fibers of glass that can break off and become airborne, which can cause irritation and potentially lead to lung damage if inhaled. Additionally, glass wool can be sharp and cause cuts or punctures if handled without gloves. Therefore, it is important to wear gloves when working with glass wool to minimize the risk of injury or irritation.
Glasswool insulation is generally considered sustainable as it is made from natural and recycled materials, primarily glass fibers. Additionally, glasswool insulation is energy-efficient and can help reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions from heating and cooling. However, it is important to note that the production of glasswool insulation does have environmental impacts, such as energy use and emissions during manufacturing, transportation, and disposal. Proper installation and maintenance can also affect the sustainability of glasswool insulation. Overall, the sustainability of glasswool insulation depends on various factors, but it can be a good option for improving energy efficiency in buildings.
No, glasswool is not waterproof. Glasswool is a type of insulation material made from glass fibers, and it is designed to trap air and reduce heat transfer. However, glasswool can absorb water and moisture, which can reduce its insulating properties and cause it to deteriorate over time. To prevent water damage, glasswool insulation should be installed in areas where it will not be exposed to moisture or it should be covered with a water-resistant barrier.
The highest R rating insulation available may vary depending on the type of insulation and manufacturer, but generally, closed-cell spray foam insulation has the highest R-value per inch of thickness among commonly used insulation materials. Closed-cell spray foam insulation typically has an R-value of 6.0 to 7.0 per inch of thickness, which can help provide superior insulation performance and energy efficiency in buildings.
Yes, glass wool can be recycled. The recycling process involves crushing and melting the glass wool, which can then be used to create new products such as insulation material. However, the feasibility of recycling glass wool depends on the quality of the material, the presence of contaminants, and the availability of appropriate recycling facilities.
Glass wool insulation can have a lower environmental impact compared to other types of insulation, but it is not entirely eco-friendly. While glass wool itself is made from natural materials such as sand and recycled glass, the manufacturing process involves high temperatures and energy consumption. Additionally, the fibers in glass wool can cause irritation and respiratory issues if not handled properly during installation or disposal.
Overall, it is important to consider the entire lifecycle of a product, including its production, use, and disposal, when evaluating its environmental impact. There are other types of insulation materials, such as cellulose or wool, which may be more eco-friendly depending on their specific manufacturing and disposal processes.
Glass wool, a type of insulation material made from glass fibers, can cause skin, eye, and respiratory irritation if proper precautions are not taken during installation or handling. Long-term exposure to glass wool fibers can lead to lung diseases such as lung cancer and pulmonary fibrosis. Therefore, it is important to use protective clothing and equipment such as gloves, goggles, and masks when handling glass wool.
Glass wool is a synthetic material made from molten glass that is spun or blown into fibers and then bonded together with a binder.
Fiberglass insulation is commonly used to insulate buildings and homes in order to improve their energy efficiency by reducing the amount of heat lost through walls, ceilings, and floors. It works by trapping pockets of air between the fibers, which slows down the transfer of heat. Fiberglass insulation can also be used in a variety of other applications, such as insulating pipes, ductwork, and appliances, as well as for soundproofing and fireproofing purposes.
Some potential disadvantages of using fiberglass insulation are:
Skin and respiratory irritation: Fiberglass insulation can cause skin and respiratory irritation if proper safety precautions, such as wearing protective clothing and masks, are not taken during installation.
Settling and compression: Over time, fiberglass insulation can settle and compress, which can reduce its effectiveness and lead to gaps in the insulation.
Moisture absorption: Fiberglass insulation can absorb moisture, which can reduce its insulating ability and promote the growth of mold and mildew.
Flammability: Fiberglass insulation is combustible and can ignite if exposed to high temperatures or flames.
Environmental concerns: The production process of fiberglass insulation can involve the use of chemicals and energy, and the disposal of fiberglass waste can be challenging and contribute to environmental issues.
Both fiberglass insulation and foam insulation have their own advantages and disadvantages, and which one is better depends on the specific needs and requirements of the situation.
Fiberglass insulation is typically more cost-effective than foam insulation and can be easier to install. It also has a longer lifespan and is more resistant to moisture and mold growth.
Foam insulation, on the other hand, has a higher R-value (thermal resistance) than fiberglass insulation, meaning it provides better insulation per inch. It also provides a better air seal, which can reduce energy loss and improve indoor air quality.
So, the simple answer is that neither fiberglass insulation nor foam insulation is definitively better than the other. The choice between them depends on various factors such as the specific application, budget, environmental concerns, and personal preferences.
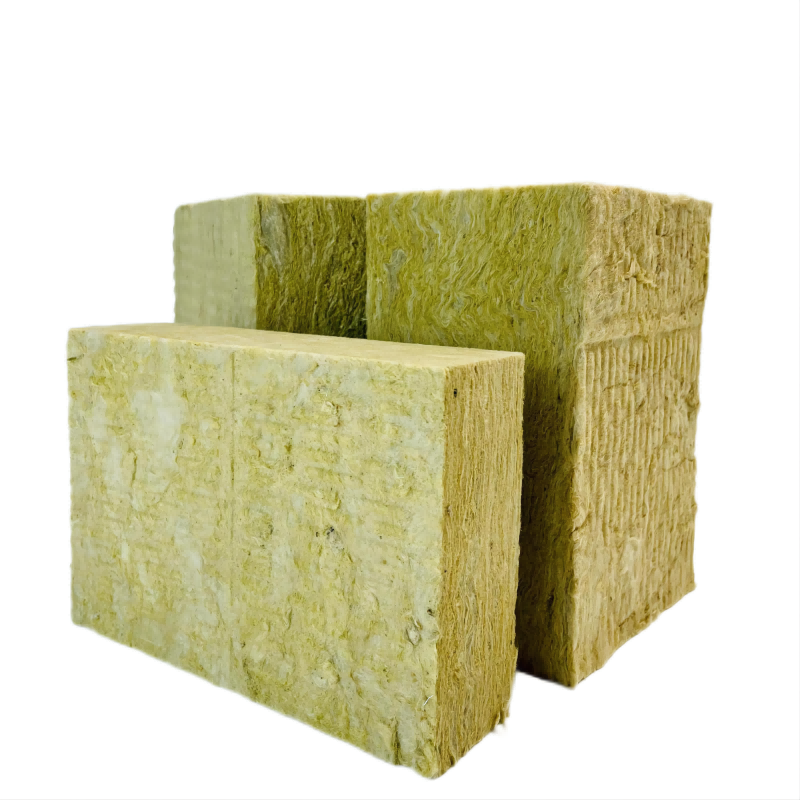
Rock Wool FAQ
1.Main material: Basalt and dolomite.
2.Fuel: Coke.
3.Binder: thermosetting phenolic resin.
4.Additive: De-dust oil hydrophobic agent (silicone emulsion Silicone)
coupling agent (silane) Ammonia, ammonium sulfate.
1.Basalt content up to 70%-90%.
2.Fiber diameter 3-6um.
3.Shot content 0.25mm diameter≤5%.
4.Organic Content (binder content) 3%-4%.
Rock wool does not contain asbestos.
CFCs, HCFCs and HFCs and other substances harmful to the environment are not used in the production process, which will not harm human health, let alone increase the risk of cancer.
Usually 120-150kg/m3 with high pull strength can be used in external wall; 80-100kg can be used in inner wall; 60-80kg can be used in Sandwich panel.
1.service tempeature different: glass wool’s maximun service temperature is 350℃, while rock wool can be as high as 650.
2.rock wool is cheaper than glass wool.
3.rock wool is heavier than glass wool, and it has higher strength than glass wool.
1.basalt rock wol is made from basalt and dolomite, slag wool is made from Blast Furnace Slag and a small percentage basalt.
2.slag wool is much cheaper than basalt rock wool.
3.basalt rock wool has good weather resistance and high strength. It’s fiber diameter is fine and has low slag ball content. Slag wool is opposite.
Rock wool is a versatile insulation material made from natural volcanic rock, which is melted and then spun into thin fibers. These fibers are then bonded together to form a dense, lightweight and durable material that can be used for a variety of applications.
One of the primary uses of rock wool is as insulation for buildings, particularly in walls, roofs, and floors. It is an excellent thermal insulator, meaning it can help to reduce heat transfer through a building's envelope, helping to keep the interior cooler in summer and warmer in winter.
Rock wool is also used as an acoustic insulation material, helping to reduce the transmission of sound between rooms or to the outdoors. It can be used in walls, ceilings, and floors to create quieter environments.
In addition to insulation, rock wool can also be used for horticulture, as a growing medium for plants. It provides excellent drainage and moisture retention, and is resistant to mold and mildew.
Rock wool can also be used as a filtration material, particularly in industrial settings where it can help to capture and filter out airborne particles and pollutants. It is also used as a fireproofing material, as it is non-combustible and can help to prevent the spread of fire.
Rock wool is a popular insulation material made from rocks and minerals, typically basalt or diabase. While it has some benefits, such as excellent thermal and acoustic insulation, there are also several disadvantages to using rock wool. Some of these include:
Health risks: Rock wool fibers can cause respiratory problems when inhaled, particularly if the material is not properly installed or handled. The fibers are small and can easily become airborne, leading to irritation of the lungs and throat. Prolonged exposure can lead to more serious health issues.
Environmental concerns: The production of rock wool requires a lot of energy and can generate significant amounts of waste. Additionally, the material itself is not biodegradable, meaning it can take many years to break down and could potentially end up in landfills.
Cost: Rock wool insulation can be more expensive than other types of insulation, such as fiberglass. This can make it less appealing for those on a tight budget.
Water absorption: Rock wool insulation can absorb water, which can lead to mold growth and other issues if not properly installed or protected.
Difficulty in installation: Installing rock wool insulation can be difficult, particularly in tight spaces or areas with complex shapes. It can be challenging to cut and shape the material to fit properly, which can make installation more time-consuming and labor-intensive.
Overall, while rock wool insulation has some benefits, it also has several disadvantages that should be carefully considered before deciding whether to use it.
Rock wool insulation can be worth the money in certain situations, depending on your specific needs and circumstances. Here are some factors to consider:
Thermal performance: Rockwool insulation has excellent thermal performance, meaning it can effectively reduce heat transfer and maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. If you live in a region with extreme temperatures, or if you want to reduce your energy bills, Rockwool insulation can be a good investment.
Fire resistance: Rockwool insulation is non-combustible and can resist temperatures of up to 2150°F. This makes it an excellent choice for fire protection and can increase the safety of your home.
Sound insulation: Rockwool insulation has great sound insulation properties, making it an excellent choice for reducing noise pollution from outside or within your home.
Moisture resistance: Rockwool insulation is resistant to moisture, which can help prevent the growth of mold and mildew in your home.
Overall, Rockwool insulation can be a great investment in your home's energy efficiency, safety, and comfort. However, it's essential to consider your specific needs, budget, and the insulation's cost-effectiveness in the long run. You should consult with a professional contractor or insulation expert to determine the best type of insulation for your needs.
Rockwool, also known as mineral wool, can vary in price depending on factors such as the quality, thickness, and size of the insulation. Generally, it is considered to be moderately priced compared to other types of insulation materials such as fiberglass and spray foam. However, it is important to note that the cost of Rockwool insulation may be higher initially, but it can offer long-term savings in energy costs by improving the energy efficiency of the building. Additionally, the cost of installation can also impact the overall cost of using Rockwool insulation. It is always best to compare prices and consult with a professional to determine the most cost-effective insulation solution for your specific needs.
Rockwool is a type of insulation material made from volcanic rock or slag. If rock wool gets wet, it can cause a reduction in its insulating properties and potentially promote the growth of mold or mildew. It is important to prevent moisture from accumulating in Rockwool insulation to maintain its effectiveness.You can choose ECOIN hydrophobic rock wool to prevent this from happening.
Rock wool has both positive and negative environmental impacts and its overall environmental friendliness depends on how it is produced, used, and disposed of.
Both rockwool and fiberglass insulation have their advantages and disadvantages. It is difficult to say which is better overall, as the choice depends on the specific application and budget. Rockwool is denser and offers better sound insulation and fire resistance, while fiberglass is typically less expensive and easier to install. Ultimately, it is important to consider factors such as R-value, environmental impact, and specific application requirements when selecting insulation material.
No, rockwool does not contain asbestos.
Mice do not necessarily avoid rockwool insulation. In fact, mice can potentially use rockwool insulation as nesting material, especially if they are seeking a warm and comfortable place to build their nests. However, rockwool insulation can also be difficult for mice to move or chew through, which may make it less attractive to them as a nesting material compared to other softer materials like paper or fabric.
It's worth noting that mice are highly adaptable and resourceful animals, and they can find their way into a wide variety of materials and structures in search of food, shelter, and nesting sites. Therefore, even if they do not prefer rockwool insulation, they may still be able to enter homes or buildings that use this type of insulation if there are other entry points or attractants present.
No, Rockwool is not as bad as asbestos. While both Rockwool and asbestos are mineral-based materials used for insulation, there are significant differences in their health effects.
Asbestos is a known carcinogen and exposure to it can lead to mesothelioma, lung cancer, and other respiratory diseases. In contrast, Rockwool does not contain asbestos and has not been linked to the same health risks.
However, like any other insulation material, Rockwool can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract if proper safety precautions are not taken during installation. It is important to follow manufacturer instructions and wear appropriate protective equipment when working with any insulation material.
There is no evidence to suggest that rockwool affects WIFI signals. Rockwool is an insulation material made from volcanic rock and it does not contain any electronic components that could interfere with WIFI signals.
However, the effectiveness of WIFI signals can be affected by various factors such as distance from the router, obstacles in the path of the signal, and interference from other electronic devices. If rockwool insulation is installed in a building, it may affect the strength of the WIFI signal if it is used as a barrier between the router and the device accessing the WIFI signal. In such cases, it is recommended to use WIFI extenders or place the router in a more central location to improve the signal strength.
Rockwool is a type of insulation material that is commonly used in buildings to reduce heat loss and improve energy efficiency. It is made from spun fibers of rock, usually basalt or diabase, and has excellent thermal insulation properties.
Rockwool works by trapping air within its fibers, which helps to slow down the transfer of heat through the insulation material. This means that heat from inside a building is less likely to escape through the walls or roof, and cold air from outside is less likely to penetrate into the building.
So, to answer your question, yes, rockwool does reduce heat by providing a barrier to slow down the transfer of heat through the building envelope.
Rockwool is a popular and versatile material used for insulation, hydroponic gardening, and soundproofing. The durability and longevity of rockwool depend on several factors, including the quality of the material, its usage, and maintenance.
In general, rockwool can be used multiple times for hydroponic gardening if it is properly cleaned and sanitized between uses. However, over time, the material may become compressed, lose its structure and insulation properties, and may need to be replaced.
For soundproofing applications, rockwool is generally a one-time-use material. Once it has been installed and used to absorb sound, it is typically not removed or reused.
It's always best to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for specific recommendations on how to use and reuse rockwool, as well as when to replace it.
Rockwool, a type of insulation made from spun mineral fibers, is not flammable. It is made from materials that are non-combustible, such as basalt rock and recycled slag. Additionally, it has a high melting point, which means it can withstand high temperatures without catching fire or releasing toxic fumes. However, while rockwool itself is not flammable, it can still pose a fire risk if it is installed improperly or in close proximity to flammable materials such as wiring or insulation. Therefore, it is important to follow proper installation guidelines and ensure that all building materials are properly separated from potential heat sources.
Yes, rockwool is generally considered to be warmer than fiberglass insulation because of its higher density and better thermal conductivity properties. ROCKWOOL insulation is made from stone wool, which is a type of mineral wool that is denser and has a higher R-value (a measure of thermal resistance) than fiberglass insulation. This means that ROCKWOOL insulation can provide better insulation and help keep your home warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer. Additionally, ROCKWOOL insulation is non-combustible, making it a safer option for insulation compared to fiberglass, which can catch fire under certain conditions.
Algae growth on rockwool cubes is a common problem in hydroponic systems. To prevent algae growth, here are some steps you can take:
Reduce light exposure: Algae require light to grow, so reducing the amount of light that reaches the rockwool cubes can help prevent algae growth. You can cover the rockwool cubes with a light-proof material or place them in a shaded area.
Maintain proper nutrient levels: Algae thrive in nutrient-rich environments. By ensuring that the nutrient solution is properly balanced, you can help prevent algae growth. Avoid overfeeding your plants, as excess nutrients can lead to algae growth.
Use hydrogen peroxide: Hydrogen peroxide can be used to kill algae on rockwool cubes. Mix one part hydrogen peroxide with nine parts water and apply to the affected areas. Be sure to rinse thoroughly with clean water afterward.
Regular cleaning: Regularly cleaning your hydroponic system, including the rockwool cubes, can help prevent algae growth. Use a mild bleach solution to clean the rockwool cubes and other system components.
By following these steps, you can help prevent algae growth on your rockwool cubes and keep your hydroponic system healthy.
No. Both mineral wool and Rockwool are effective insulation materials and can be suitable for different applications and preferences. The choice between them depends on various factors such as the specific use case, insulation requirements, availability, cost, and personal preference.
Rock wool insulation can be installed in various places including walls, attics, floors, and ceilings to improve energy efficiency and soundproofing.
Mineral wool board, also known as mineral fiber board or mineral wool insulation board, is a type of insulation material that is made from mineral fibers. These fibers are typically derived from natural minerals such as basalt or diabase, which are melted and spun into thin fibers.
The resulting fibers are then compressed and formed into a board or batt, which can be used for thermal insulation in buildings and other structures. Mineral wool board has excellent thermal insulation properties and is resistant to fire, moisture, and pests. It is commonly used in commercial and residential buildings to insulate walls, floors, and ceilings.
Mineral wool board is also known for its sound-absorbing properties and is often used in buildings to reduce noise transmission between rooms or to the exterior. It is a popular choice for green building projects because it is made from natural, renewable materials and has a low environmental impact.
Mineral wool board is a type of insulation material made from rock or slag fibers, which are compressed and bonded to form a rigid board. It is commonly used in buildings to provide thermal and acoustic insulation for walls, roofs, and floors. Mineral wool board has excellent fire resistance properties and can also provide effective soundproofing. It is a durable and cost-effective insulation solution that can help to reduce energy consumption and improve the comfort and safety of buildings.
Yes, Rock wool insulation can be used for loft insulation. In fact, it is a popular choice for this purpose due to its excellent thermal and acoustic insulation properties.
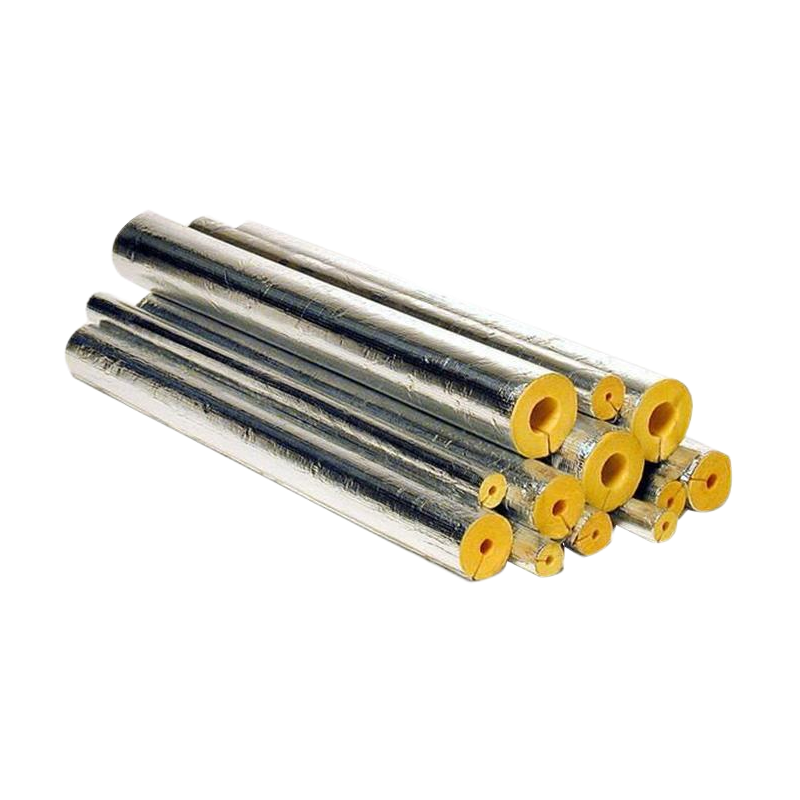
There are various materials that can be used to insulate pipes, depending on factors such as the temperature of the pipes, the environment they are in, and the specific requirements of the application. Some common materials used for pipe insulation include:
Fiberglass: Fiberglass insulation is a popular choice for insulating pipes, as it is lightweight, easy to install, and has good thermal performance.
Mineral wool: Mineral wool is a type of insulation made from volcanic rock or other mineral materials. It is fire-resistant and can withstand high temperatures.
Polyurethane foam: Polyurethane foam is a type of insulation that can be sprayed or injected into a cavity to create a seamless insulation layer. It has good thermal performance and is often used for high-temperature applications.
Cellular glass: Cellular glass is a type of insulation made from crushed glass mixed with a foaming agent. It is highly resistant to moisture and can withstand high temperatures.
Closed-cell elastomeric foam: This type of foam insulation is made from a synthetic rubber material and is often used for refrigeration and HVAC applications. It has good thermal performance and is resistant to moisture and UV radiation.
The choice of insulation material will depend on factors such as the temperature range of the pipes, the environment they are in, and the specific requirements of the application. It's important to choose the right insulation material to ensure that the pipes are properly protected and energy efficient.
Insulation in pipes serves to reduce the transfer of heat or cold from the fluid inside the pipe to the environment outside of it. This can help to maintain a consistent temperature for the fluid being transported, prevent freezing or overheating, and improve energy efficiency. Insulation can also help to prevent condensation from forming on the outside of the pipe, which can cause corrosion and other damage. Additionally, insulation can reduce noise transmission through the pipe and provide some degree of fire protection.
Closed-cell foam insulation typically has the highest R-value per inch of thickness compared to other types of pipe insulation. This is because the closed-cell structure of the foam material traps air pockets, which reduces the transfer of heat through the insulation. Some examples of closed-cell foam insulation include polyisocyanurate, extruded polystyrene, and cellular glass insulation. The specific R-value of each type of insulation can vary depending on the manufacturer and thickness of the material, but closed-cell foam insulation generally offers the highest thermal resistance per inch of thickness.
Both pipe insulation foam and rubber have their advantages and disadvantages. Foam insulation is generally more affordable and easier to install, but it may not be as durable as rubber insulation. Rubber insulation, on the other hand, is more expensive but also more durable and resistant to moisture and extreme temperatures. Ultimately, the choice between foam and rubber insulation will depend on the specific needs of your project, including factors such as budget, desired lifespan, and environmental conditions.
Both fiberglass and foam are commonly used for pipe insulation, but the choice ultimately depends on the specific needs of the application.
Fiberglass is a good option for high-temperature applications and is resistant to fire and moisture. It is also relatively affordable and easy to install.
Foam insulation, on the other hand, offers superior thermal resistance and is better at preventing heat loss. It can also be used in areas with limited space for insulation. However, it is generally more expensive than fiberglass and can be more difficult to install.
In summary, fiberglass is a good option for general use and high-temperature applications, while foam insulation is better suited for situations where maximum thermal resistance is required.
Pipe insulation is typically designed to withstand temperatures ranging from -70°F to 250°F (-56°C to 121°C), depending on the type of insulation material used. However, specific temperature ranges may vary based on the insulation type, application, and manufacturer's recommendations.
The R-value of pipe insulation is calculated by dividing the thickness of the insulation by its thermal conductivity. The resulting value represents the insulation's resistance to heat flow, with a higher R-value indicating better insulation performance.
The K value, also known as the thermal conductivity, measures the ability of insulation material to conduct heat. It indicates how much heat can pass through a unit area of the material in one hour when the temperature difference between both sides of the material is one degree Celsius.
Pipe insulation can be very efficient in reducing heat loss or gain and saving energy, especially in hot and cold water systems, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, and industrial processes. Insulation materials with higher R-values (thermal resistance) can provide better insulation performance, and thicker insulation can further improve energy savings. Proper installation and maintenance are also crucial for achieving optimal efficiency. Overall, pipe insulation is a cost-effective way to improve energy efficiency and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
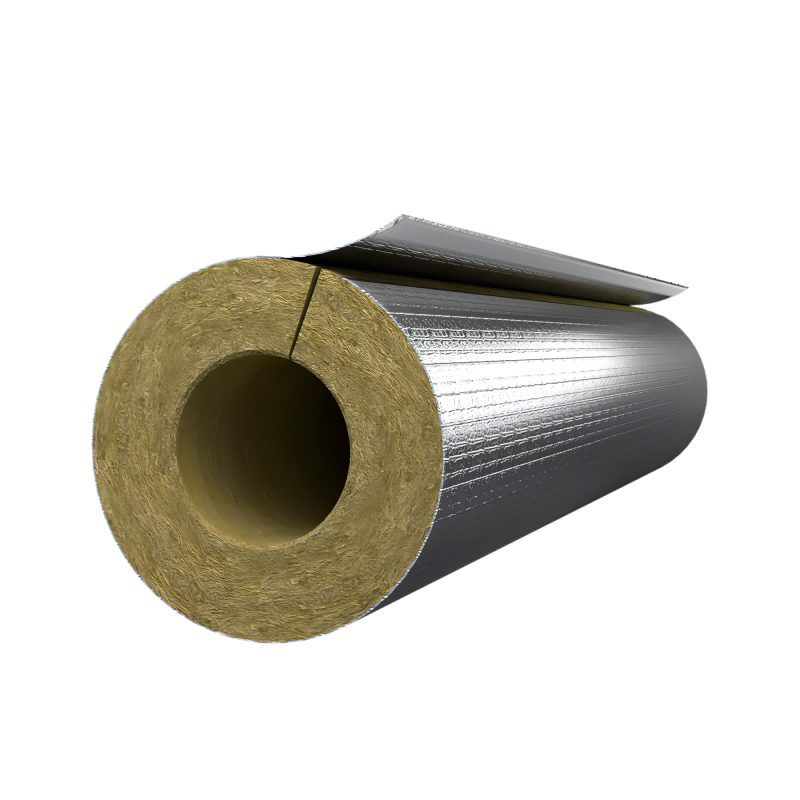
Aluminum roll jacketing / insulation accessories FAQ
1.PE is easy to peal off, while polysurlyn film is hard to peal.
2.The only function of PE film to anti-scratch. The function of polysurlyn is preventing moisture and corrosion inside jacketing from direct contact with insulation causing galvanic or chemical corrosion, thus extends the usage expectancy of metal jacketing.
3.The processing cost of applying PE is much cheaper than polysurlyn.
We strongly recommend heat applying to you. Heat apply is not easy to peal off.
Ecoin will guarrantee the thickness ±0.01mm
For the items which will be applied with moisture barrier, you need to tell us the thickness you want is before, or after applied moisture barrier.
We will apply the polysurlyn to smooth aluminum coil first, then get it stucco embossed.
Three layer film to provide optimized performance
• Thick film (3 mils, 76 μm) for long-term durability
• Zero pinholes – much fewer than polykraft and painted
• Much lower water vapor transmission rate than polykraft
• No Kraft paper present to absorb water
• Tough and strong film to resist installation damage
• Great adhesion to metal substrate
• Low flammability
Ten 12”x 12” sheet samples with the Polysurin film were examined under a binocular microscope with up to 25X magnification. In 50 sq. ft, up to 5 pinhole detections are allowed. The moisture retarder shall have no visual defects that will affect the performance; it shall be free of laminated separations, holes, rips, tears, scratches or dents are allowed. No such defects were observed; the samples provided meet the detection criteria of ASTM C1729
Jacketing in insulation refers to the protective outer layer that is added to insulation material. The jacketing is typically made of a durable material such as metal, plastic, or rubber and serves to protect the insulation from damage, weathering, and other external factors.
Jacketing is often used in applications where the insulation will be exposed to the elements, such as in outdoor piping systems or in industrial settings. The jacketing helps to prevent moisture from penetrating the insulation, which can reduce its effectiveness and lead to damage over time.
In addition to providing protection, jacketing can also provide additional insulation value. For example, a reflective jacketing material can help to reflect heat back into space, improving the overall efficiency of the insulation system.
Overall, jacketing is an important component of many insulation systems and can help to improve their performance and lifespan.
Insulation jacketing is used to protect the insulation material and ensure it remains effective in maintaining temperature control, as well as protecting the insulation from environmental factors like moisture and physical damage. There are several types of insulation jacketing materials, including:
Metal cladding: This type of jacketing is made of metal sheets, usually aluminum or stainless steel. It provides excellent protection against mechanical damage, UV radiation, and weathering.
PVC: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a common type of plastic jacketing. It's lightweight, flexible, and easy to install. PVC jacketing is often used in indoor applications where exposure to harsh environmental conditions is not a concern.
Polyethylene: Polyethylene (PE) is another type of plastic jacketing. It's a more durable option than PVC and can withstand exposure to harsh environmental conditions, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Fiberglass: Fiberglass is a non-metallic jacketing material that's commonly used in industrial applications. It's resistant to heat, moisture, and chemicals, making it a good choice for applications where these factors are a concern.
Mineral wool: Mineral wool is a fibrous material made from molten rock or slag. It's a good insulator and is often used in high-temperature applications. Mineral wool jacketing is typically coated with a weather-resistant coating to protect it from the elements.
Elastomeric: Elastomeric insulation jacketing is made of a synthetic rubber material that's resistant to UV radiation, moisture, and chemicals. It's a good option for outdoor applications.
Overall, the type of insulation jacketing material you choose will depend on the specific needs of your application, including environmental factors, temperature range, and mechanical requirements.
Aluminum jacketing refers to the process of covering or wrapping a material or equipment with a layer of aluminum sheet or coil. This is typically done to protect the underlying material or equipment from damage, corrosion, and weathering, as well as to provide a clean and aesthetically pleasing appearance.
Aluminum jacketing is commonly used in the insulation industry, where it is applied to the exterior of insulated piping, ductwork, tanks, and vessels. The aluminum jacketing serves as a vapor barrier and protects the insulation from physical damage and environmental factors.
Aluminum jacketing can be made from a variety of alloys, including 3003, 3105, and 1100. These alloys are typically lightweight, durable, and resistant to corrosion, making them an ideal choice for outdoor or industrial applications.
Aluminum jacketing can be applied using a variety of methods, including roll-bonded, spray-applied, or mechanically fastened. The choice of method depends on the specific application and the desired performance characteristics.
Aluminum jacketing thickness can vary depending on the specific application and requirements, but typically it ranges from 0.016 inches (0.4 mm) to 0.032 inches (0.8 mm). The thickness is chosen based on factors such as the type of insulation material, the environment in which the jacketing will be used, and the level of protection needed for the underlying insulation. Thicker aluminum jacketing is generally used for more demanding applications where greater protection is required.
The thickness of pipe insulation aluminum jacket can vary depending on a few factors such as the size of the pipe, the temperature of the substance flowing through the pipe, and the insulation material being used.
Generally, the thickness of the aluminum jacket can range from 0.016 inches to 0.032 inches. However, thicker jackets can be used for larger pipes or for pipes carrying substances at higher temperatures. It's important to consult with a professional or reference insulation manufacturer specifications to determine the appropriate thickness for your specific application.
Stainless steel is not typically used as insulation material. Insulation is used to reduce the transfer of heat or sound between two surfaces, and materials such as fiberglass, mineral wool, or foam are commonly used for this purpose.
However, stainless steel can be used as a cladding or jacketing material over insulation to provide additional protection and durability in certain applications. For example, in industrial settings, insulation on piping or equipment may be exposed to harsh conditions such as high temperatures, chemicals, or physical wear and tear. By using a stainless steel jacket, the insulation can be protected from these elements and maintain its effectiveness over time. Additionally, stainless steel is resistant to corrosion and can provide a clean and polished appearance, making it a popular choice for applications where aesthetics are important.
A moisture barrier for metal jacketing is a layer of material that is placed between the metal jacketing and the insulation material used to insulate piping or equipment. This barrier is designed to prevent moisture from penetrating the insulation material and reaching the metal surface beneath it.
Moisture barriers are typically made from a thin layer of polyethylene, polypropylene, or other materials that are resistant to moisture. They are applied to the surface of the insulation material before the metal jacketing is installed, and are typically secured in place with adhesive or tape.
The moisture barrier helps to protect the insulation material from moisture damage, which can reduce its effectiveness and lead to corrosion of the metal surface. By preventing moisture from reaching the metal surface, the barrier can also help to extend the life of the piping or equipment being insulated.
Yes, polyethylene is a good moisture barrier. Polyethylene is a type of plastic that is commonly used as a moisture barrier in various applications such as packaging, agriculture, and construction. It has a very low moisture vapor transmission rate, which means that it can effectively prevent the passage of water vapor through it.
Polyethylene is also resistant to water and other liquids, making it an ideal choice for applications that require a material that can withstand moisture exposure. In addition, polyethylene is lightweight, flexible, and easy to handle, which makes it a popular choice for packaging materials.
Overall, polyethylene is an effective moisture barrier that is widely used in various industries due to its excellent moisture resistance properties.
Corrugated aluminum sheet refers to a type of aluminum panel that has been formed into a wavy or rippled pattern, similar to the shape of corrugated cardboard. This type of sheet is often used in construction, roofing, and siding applications due to its durability, lightweight, and resistance to corrosion. Corrugated aluminum sheet can also be used in decorative applications, such as interior wall paneling or ceiling tiles, and can be painted or coated with various finishes to achieve a desired aesthetic.
The size of a corrugated aluminum sheet can vary depending on the manufacturer and the intended use. However, standard sizes are commonly available in the market.
The length of a corrugated aluminum sheet usually ranges from 6 feet to 20 feet (1.8 to 6 meters), while the width typically ranges from 2.5 to 4 feet (0.76 to 1.22 meters). The thickness can range from 0.16 to 0.6 inches (0.4 to 1.5 centimeters) depending on the intended application.
It's worth noting that some manufacturers may produce custom sizes upon request, and the thickness and shape of the corrugations can also vary depending on the application. For insulation application, the most common used thickness is 0.4-1.2mm, courrugated type includes V4.8, V32,V65 and box ribbed.

Need more help?
Feel free to contact us for more information
Vehicula malesuada eu magna commodo mattis elementum ante mi nullam interdum. Mauris maecenas lacus porttitor elit torquent aenean. Tempor facilisis fringilla a sagittis nibh mauris elit pellentesque. Eget quam adipiscing eu consequat facilisi suscipit fames.
Top Thermal Insulation Materials Manufacturers
Ecoin is a global leading thermal insulation factory in North China, which is committed to manufacturing premium-quality thermal insulation for commercial, industrial, and residential applications.
We have trustworthy partners of customers from over 150 countries.